The General Data Protection Regulation is a complex piece of data privacy legislation from Europe that impacts businesses around the world, and businesses need to understand it’s requirements in order to achieve compliance.
This GDPR for Dummies guide explains everything you need to know about the GDPR in easy-to-understand language.
Below, I provide a beginner’s explanation of the GDPR, who it applies to and protects, and what steps you need to take to set your business up for full compliance.
- Key Takeaways: GDPR Explained in Under 5 Minutes
- The GDPR Explained for Beginners
- How Does the GDPR Affect Internet Users?
- How Does the GDPR Affect Businesses?
- Quick GDPR Checklist for Dummies: The Do's and Don'ts
- Dummies Guide to the GDPR [Infographic]
- GDPR for Dummies FAQ
- How Can Termly Help You Comply With the GDPR?
- Summary
Key Takeaways: GDPR Explained in Under 5 Minutes
I don’t think businesses should always have to rely on a lawyer to comprehend the basic requirements to comply with the GDPR, so I’ve explained the key takeaways from the regulation in easy-to-understand language for you below:
- What is the GDPR? — The GDPR is a data privacy regulation from Europe that grants rights to individuals in the EU/EEA over how their personal information gets processed, irrespective of whether the processing occurs online or offline. It is technology-neutral and explains the requirements natural persons, businesses, public authorities, or organizations must meet to process that information legally.
- Who does the GDPR protect? — The GDPR protects any individual physically located in the European Union (EU) or the European Economic Area (EEA), regardless of nationality, citizenship status, or whether their information is processed online or offline.
- Who does the GDPR apply to? — The GDPR applies to any business in the EU/EEA which processes personal data as part of the activities of one of its branches, regardless of where the personal data is processed. It also applies to businesses established outside of the EU/EEA that process personal information from individuals (irrespective of whether they’re registered users to a specific website or not) and either offer goods and services accessible in the EU/EEA or monitor the behavior of individuals in the EU/EEA.
- What rights does the GDPR grant to individuals? — Under the Regulation, individuals (called data subjects) have the right to access, correct, amend, restrict, and delete their personal information. They also have the right to data portability, which means they can copy, move, and transfer their information in a way that makes it easier to reuse in a different format.
- What are the GDPR requirements for businesses? — Entities that fall under the scope of the GDPR must explain their data collection processes in a transparent and compliant privacy policy that clearly states, in part, the legal basis for processing each category of personal information and the purposes of that processing. They must also provide appropriate technical and organizational measures to securely store the personal data that they process so it’s safe from data breaches or leaks.
- What legal policies and solutions does my website need to comply with the GDPR? — To start your ongoing GDPR compliance journey, your website needs a privacy policy, cookie policy, cookie banner, data processing agreements (DPA), and data subject access request (DSAR or SAR) forms.
- What are the penalties for violating the GDPR? — Businesses that don’t comply with the GDPR risk fines of up to €20 million ($23 million) or 4% of your gross annual income from the previous year, whatever is highest.
The list above is a good place to start for understanding the GDPR.
But in the rest of this simplified GDPR guide, I go into more detail about important parts of the Regulation in more detail.
The GDPR Explained for Beginners
Next, I’ll cover the basics of the GDPR, like what it is, why we need it, and how it defines specific essential phrases related to personal information and data processing.
What Is the GDPR?
The GDPR is an acronym for the General Data Protection Regulation and is a piece of European legislation that protects personal information. It outlines several requirements businesses must follow to process that data legally.
Although passed in the EU, it affects businesses worldwide and introduced the concept of Privacy by Design (PbD).
This privacy approach involves keeping data collection to a minimum and building security measures from the inception of the processing activity to prevent data leaks and breaches at all stages of the processing of personal information.
The GDPR follows seven principles of data protection:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (aka, security)
- Accountability
It went into effect on May 25, 2018, and set new standards for data privacy and security, kickstarting a wave of global privacy laws that forever changed how consumers and businesses alike use the Internet.
Why Do We Need the GDPR?
We need laws like the GDPR because people have the right to know about and have some control over what information gets collected about them and how it’s further used, or who it gets shared with. That includes you, me, and anyone else using the Internet.
Personal data is highly valuable — it supports a trillion-dollar industry.
Nowadays, numerous companies make a portion of their profits by selling personal information to advertisers. Regulations like the GDPR create a privacy framework for companies of all sizes by creating rules about what they can and can’t do with your personal information.
Knowing how this key piece of legislation works and what your potential rights are helps you maintain more control over your life both online and offline.
Who Does the GDPR Protect?
The GDPR protects the personal information of any person within the EU or EEA and refers to them as data subjects.
The EU Member States are:
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Republic of Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
The EFTA (European Free Trade Association) countries who are part of the EEA (European Economic Area) are:
- Iceland
- Liechtenstein
- Norway
The individual’s physical location is the only factor taken into account by the Regulation — it applies regardless of nationality or citizenship status.
What Businesses Must Follow the GDPR Requirements?
The GDPR applies to any business established in the EU/EEA, irrespective of whether the processing occurs within or outside the EU/EEA.
It also applies to businesses not established in the EU/EEA that process personal information and either:
- Offers goods or services that are available to data subjects within the EU or EEA (irrespective of whether a payment of the data subject is required) or
- Monitors the behavior of data subjects within the EU or EEA
Companies located in any part of the world may fall under the legal scope of the GDPR.
However, if your business is not established in the EU/EEA and any goods or services provided by you are unavailable to individuals in the EU/EEA, and you don’t process data from anyone in the EU/EEA, you don’t need to follow the GDPR.
GDPR Definitions for Dummies
In the table below, I provided simplified versions of the specific legal definitions of important words as they appear in the text of the GDPR to help you determine if your business needs to follow the regulation.
| Word | Definition for Dummies | Legal Definition as it appears in the GDPR (Chapter 1, Article 4) |
| Personal Data | Information that can identify a natural person (aka data subject), either directly or indirectly, such as:
|
“…any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘data subject’); an identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person…” |
| Processing |
Processing includes any of the following actions in regard to personal data relating to a data subject:
|
“…any operation or set of operations which is performed on personal data or on sets of personal data, whether or not by automated means, such as collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction…” |
| Data Controller | Any entity (natural or legal person, public authority, agency, or other body) that determines the purpose(s) and means of the processing of personal data.
Is your business the one that decides why and how the personal data is processed? Your business may be a data controller under the GDPR. |
“…the natural or legal person, public authority, agency or other body which, alone or jointly with others, determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data; where the purposes and means of such processing are determined by Union or Member State law, the controller or the specific criteria for its nomination may be provided for by Union or Member State law…” |
| Data Processor | Any third-party entity that processes the personal data of data subjects on behalf of the data controller.
Does your business receive clear instructions regarding why and how the personal data shall be processed? Your business may be a data processor under the GDPR. |
“…a natural or legal person, public authority, agency or other body which processes personal data on behalf of the controller…” |
What Are the Penalties for Violating the GDPR?
I’ll keep this section short and sweet. Depending on the type of infringement, businesses that violate the GDPR may receive fines of up to:
- €10 million ($12 million) or 2% of your gross annual income from the previous financial year (whichever is higher) for any infringement under Article 83(4).
- €20 million ($23 million) or 4% of annual gross income from the previous financial (whichever is higher) for any infringement under Article 83(5).
The Regulation is enforced by different Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) located in the EU/EEA countries.
Like a data privacy sheriff, they enforce and supervise the application of the GDPR and relevant national laws in their country, provide expert advice on data protection issues, handle complaints lodged against violations of the law, and can even hand out hefty fines.
Nomination of a DPO (Data Protection Officer)
Entities (irrespective of whether they act as controllers or processors) that process special categories of personal data or monitor the behavior of individuals on a large scale as their core activities must appoint a data protection officer (DPO) to:
- Handle all their GDPR activities and paperwork
- Monitor the compliance of the business in relation to the applicable data protection laws
- Provide internal guidance related to the applicable data protection rules or practices or
- Communicate with the appropriate data protection authority or data subjects, if necessary.
Even when a business may not be obliged to appoint a DPO under the GDPR, appointing one is still recommended as a best practice.
How Does the GDPR Affect Internet Users?
The GDPR affects Internet users based in the EU/EEA by granting them specific rights and control over when and how their personal data is processed.
Data subjects protected by the GDPR have the right to:
- Access what information is collected about them, who it’s shared with, and how it’s used
- Rectify any inaccurate information concerning the data subject
- Erase personal data concerning the data subject in certain situations
- Restrict the processing of personal data in certain circumstances
- Receive a portable copy of their data to be easily shared with another party and used in other formats
- Object to data processing in certain situations
- Opt out of automated processing, like profiling
- Withdraw consent that was previously given
- Lodge a complaint with a data protection authority
You can read more about the rights granted to data subjects in Chapter 3 of the GDPR.
How Does the GDPR Affect Businesses?
The GDPR outlines several business requirements you must follow (depending on whether you act as a controller or processor) to legally process personal information, which I cover briefly in the following sections.
Determine Your Legal Basis
According to the GDPR, your business must have a legal basis for processing each category of personal data from data subjects, so determine what these look like for your business.
The legally-sound reasons for data processing are explained in Chapter 2, Article 6 of the regulation and include:
- Obtaining affirmative consent from the data subject for one or more specific purposes
- To fulfill necessary contractual obligations to which a data subject is party to
- For legal obligations or requirements to which the controller is subject
- The vital interests of the data subject or of another natural person (usually only applies to life or death situations)
- The performance of a task carried out in the public interest or in the exercise of official authority vested in the controller
- Legitimate interests pursued by the controller or third party and these does not override the interests or fundamental rights and freedoms of the data subject(s) in question
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
If a company’s data processing activities are likely to pose a high risk to people’s fundamental rights and freedoms, they must fill out a DPIA following Chapter 4, Article 35.
Examples of high-risk processing activities include:
- Using innovative technology
- Tracking anyone’s location or behavior
- Processing genetic or biometric data (think 23andMe or DNA testing, facial recognition, fingerprints, or retinal scans)
- Marketing to children or other vulnerable individuals.
Consent and the GDPR
Many businesses under the GDPR rely on obtaining user consent to process personal information legally. If you choose to do this, you must meet precise requirements.
The GDPR defines consent as:
“… freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous indication of the data subjects wishes by which he or she, by a statement or by a clear affirmative action, signified agreement to the processing of personal data relating to him or her…”
Simply put, the data subjects concerned by your data processing must know what they agree to and freely give consent by taking an affirmative action, like selecting a checkbox or clicking a clearly marked ‘Agree’ button.
The GDPR also explains several conditions for consent in Chapter 2, Article 7, so ensure you’re meeting all of these additional requirements:
- You must demonstrate that you actually got lawful consent from the data subjects concerned.
- When asking for consent, it must be clearly distinguishable from asking your users to opt into other things, like marketing emails. For this reason, it is important to create specific and separate boxes for each different purpose.
- You have to inform the data subjects that they can withdraw their consent anytime, and you must provide an easy way to do so for the data subjects.
Most businesses use a consent banner with links to their cookie usage or personal data collection to obtain appropriate opt-in consent under the GDPR.
GDPR Privacy and Cookie Policy Requirements for Businesses
Your business needs an accurate, GDPR-compliant privacy policy and cookie policy so data subjects can understand the data processing activities performed by your business properly under the GDPR.
According to Chapter 3, Article 13 of the GDPR, businesses must present the following information to data subjects at the points where the personal data is obtained:
- The identity of and contact information for the data controller (aka, your business, if you are responsible for the means and purposes of that processing)
- The contact information of the data protection officer or DPO, when applicable
- The purpose and the legal basis for processing the personal data, as explained in Chapter 2, Article 6
- The legitimate interests of the data controller (or third-party processor), when applicable
- Who receives the data and any intention to further process that personal data
- Information about the intention to transfer the data outside of the EEA
- The amount of time data will be stored for or the criteria to determine that period
- The rights of the data subjects concerned under the GDPR
- The right to withdraw their consent if the processing is based on this legal basis
- The right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority
- The existence of automated decision-making, including profiling.
The Regulation also gives data subjects the right to obtain confirmation from the controller as to whether or not their personal data is processed and, if that is the case, to access the personal data collected about them.
Chapter 3, Article 15 states that controllers must inform the data subjects concerned all of the following details:
- Your purpose for processing the data
- The categories of data you process
- Who receives the data
- How long the data is stored for
- An explanation of the rights data subjects have over their data and how to act on them
- An explanation of the right for data subjects to complain about your business with a supervisory authority
- The source of any personal data about a data subject you have that you did not collect directly from them
- If you use any automated decision-making processes, like profiling
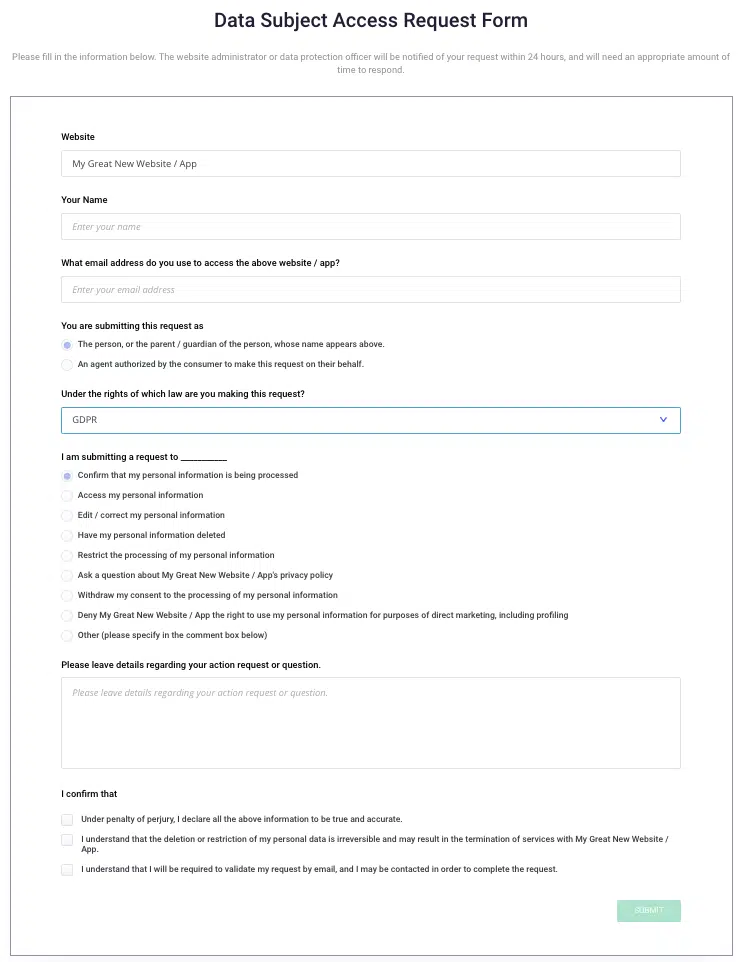
GDPR-compliant DSAR Forms
To ensure that your users protected by the GDPR can easily follow through on their rights, provide them with a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) form on your website.
A DSAR form creates a straightforward, simple process for your users who want to delete, amend, or access their information.
Termly’s CMP provides you with a free DSAR form that you can embed on your website to adequately handle requests from your data subjects, as shown in the screenshot below.
Data Processing Agreements Under the GDPR
If another company helps you process your users’ personal information, you must create a contract that follows specific requirements, as explained in Chapter 4, Article 28 of the GDPR.
You and the third party must sign the contract, often called a Data Processing Agreement (DPA). It must include all of the following details regarding the third-party processor:
- Only process personal data as instructed by the controller.
- Commit to confidentiality regarding the personal data.
- Take all security measures as outlined in Article 32 of the GDPR.
- Not engage with a sub-processor without prior written or general authorization.
- In case of outsourcing to another sub-processor, the same data protection obligations as set out in the contract or other legal act between the controller and the processor shall be imposed on the sub-processor by way of contract or other legal act.
- Must be able to assist the controller by taking appropriate technical measures to fulfill and respond to requests from data subjects to act on their rights.
- Must assist the controller in compliance with security and prior consultation requirements (written in Articles 32 and 36).
- Delete or return all personal data to the controller after the contract term ends.
- Make all information necessary to demonstrate GDPR compliance available to the controller, and inform the controller immediately if they feel an instruction infringes upon the GDPR or other Member State laws.
- Allow for and contribute to audits, including inspections conducted by the controller or another auditor mandated by the controller.
GDPR Data Safety and Security Requirements
The GDPR requires businesses to securely store the personal data they process and protect it from cybercrimes like data leaks or breaches.
It’s up to you what safety measures you put into place, but the Regulation suggests taking the following actions in Chapter 4, Article 32:
- Pseudonymization and encryption
- Ensure ongoing confidentiality, integrity, and resilience of your processing systems
- Provide a way to restore the availability and access to the data following an incident
- Create a process for testing, assessing, and evaluating the effectiveness of your technical and organizational measures.
It is recommended to assess the technical and organizational measures intended to continuously safeguard personal data (for example, once a year or in case of a specific incident or breach). Special attention shall be given to the following risks that are associated with the processing of personal data:
- Accidental or unlawful destruction
- Loss
- Alteration
- Unauthorized disclosure of or access to the personal data that is transmitted, stored, or otherwise processed
If a data breach occurs and any of the above risks materialize, you have 72 hours to inform the relevant data protection authority from the moment you become aware of the breach.
If the data breach is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of natural persons, the latter must be informed about the cybercrime as quickly as possible.
Quick GDPR Checklist for Dummies: The Do’s and Don’ts
To help simplify the GDPR even further, I’ve created two lists for you, one featuring the GDPR Dos and another featuring the GDPR Don’ts.
The GDPR Do’s
If your business falls under the scope of the GDPR, amongst others, you must do all of the following:
- DO make and publish a compliant privacy policy: Ensure your privacy policy is easy to read and understand and present it to your users wherever you collect information.
- DO publish a cookie policy and update it regularly: Cookies qualify as personal information under the GDPR, and nearly every website uses them, so verify that all cookies or trackers are communicated to your users within a cookie policy, and keep it updated so it’s always accurate.
- DO use a properly configured consent banner: If consent is your legal basis for processing personal information, use a consent banner on your website that obtains and tracks appropriate opt-in consent from users and gives them access to a preference center to change their minds.
- DO put DSAR forms on your website: Your users have the right to request to access, delete, amend, or correct the personal data you’ve collected about them, so post a DSAR form on your site to give them a way to follow through on their legal rights.
- DO use DPAs for your contracts with any third parties: If you partner with any third parties to process your users’ data, provide them with a DPA that meets all contractual guidelines explained in Chapter 4, Article 28 of the GDPR.
- DO ask yourself if the purpose for which the personal data may be collected is justified.
- DO ensure that the personal data is secured properly.
- DO keep the personal data accurate and up to date.
- DO delete personal data when it’s no longer necessary.
The GDPR Don’ts
Now that you know what to do if your business falls under the GDPR, take a look at a list of what not to do:
- DON’T use sneaky workarounds: Trying to ‘outsmart’ the system isn’t worth it — for example, if your users have to click through multiple unnecessary links to get to your consent preference center or you make it extra hard to find the opt-out button on your consent banner, you risk getting fined for non-compliance.
- DON’T use pre-checked boxes to obtain user consent: The GDPR doesn’t allow pre-checked boxes on consent banners because they prevent your users from taking an affirmative action to show they agree to your data processing activities.
- DON’T lie about how you use personal data: It’s against the GDPR to lie about what data you collect and how you use it, and the supervisory authorities from the various EU/EEA countries may hold you financially accountable.
- DON’T copy legal policies from other businesses: Legal policies are copyrighted documents; copying them directly from another entity is plagiarism. More importantly, another business’s policy won’t accurately reflect your data practices.
- DON’T keep personal data you no longer need: The GDPR clearly states that you can only store data for as long as necessary to achieve the purpose you explained to your users in your privacy policy, so ensure you don’t keep this data for longer than needed.
- DON’T think you’ll get away with non-compliance: You might assume your business is too small or too under the radar to be fined for non-compliance, but that’s not the case. Since 2018, the GDPR has generated nearly $3 billion in fines. It only takes one complaint from a user or falling victim to a single cybercrime that leaks the personal information you’ve collected for data protection authorities to hold your business accountable — the financial and reputational consequences are very real.
Dummies Guide to the GDPR [Infographic]
Good news: We’ve compiled the essential parts of this GDPR guide for dummies into an easily shareable infographic. Check it out below!
Download the GDPR for Dummies Inforgraphic using the link below:
When it comes to respecting data privacy laws and user rights, we’re all in this together — so feel free to share this guide and infographic with others if you find it helpful.
GDPR for Dummies FAQ
I love talking about data privacy compliance and the GDPR. So, below, read through some answers to the most frequently asked questions we get about the GDPR.
What does GDPR stand for?
The GDPR is an acronym for the General Data Protection Regulation.
What is the GDPR in simple words?
The GDPR is a data privacy regulation from Europe that describes the rights individuals based in the EU/EEA have over their personal information processed by businesses (or natural persons outside of their personal use) and explains what guidelines businesses worldwide must follow to process their personal data legally.
What are the seven principles of the GDPR?
The seven principles of the GDPR, as described in Chapter 2, Article 5, are:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (aka, security)
- Accountability
Who does the GDPR apply to?
The GDPR applies to any processing of personal data by a controller or processor established in the EU/EEA, irrespective of whether the processing itself takes place outside of the EEA.
The GDPR also applies to the processing of personal data by a controller or processor that is established outside of the EU/EEA but who processes the personal data of natural persons in the EU/EEA and meets either of the following conditions:
- Makes their goods or services available to consumers located in the EU/EEA, even if no monetary exchange takes place
- Monitors the online behavior of users located in the EU/EEA
Who does the GDPR protect?
The GDPR protects natural persons who are present within the European Union (EU) or the European Economic Area (EEA).
Do I need to comply with the GDPR if my business is in the US?
Yes, you need to comply with the GDPR if your business is in the US and you process personal information and meet either of the following requirements:
- You offer goods or services to consumers in the EU/EEA, even if no monetary exchange takes place
- You monitor the online behavior of individuals located in the EU/EEA
How Can Termly Help You Comply With the GDPR?
Termly offers policy generators and consent management solutions backed by our team of lawyers and data privacy experts that can help your business fully comply with the GDPR and several other data privacy laws worldwide.
We make legal compliance easy and affordable so you can remain focused on the things that matter most, like your business and customers.
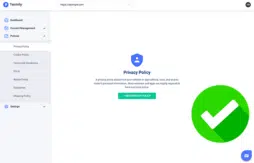
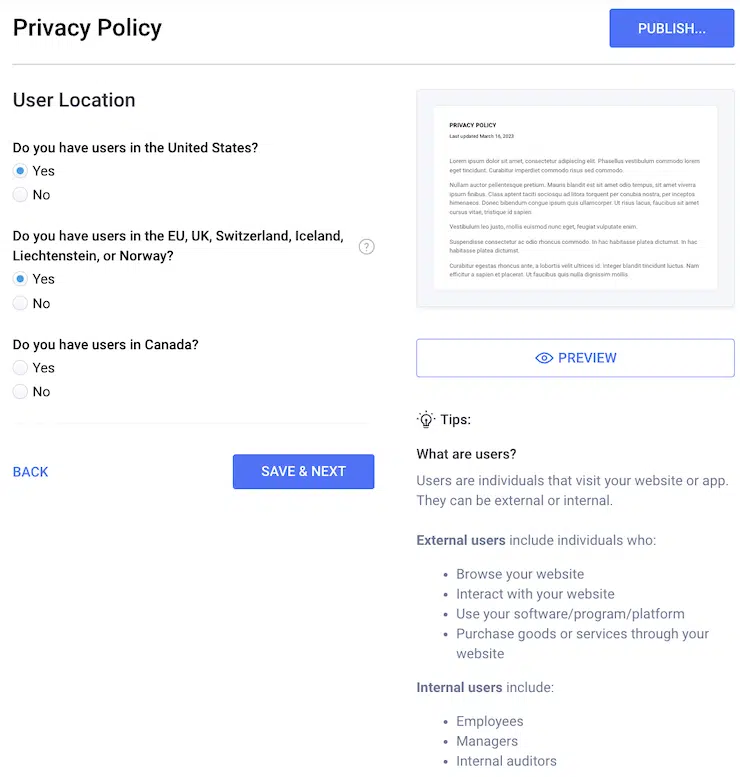
Our free Privacy Policy Generator follows all requirements outlined by the GDPR — all you need to do is answer simple questions about your business. It creates a properly formatted, compliant policy for you.
See what it looks like in the screenshot below.
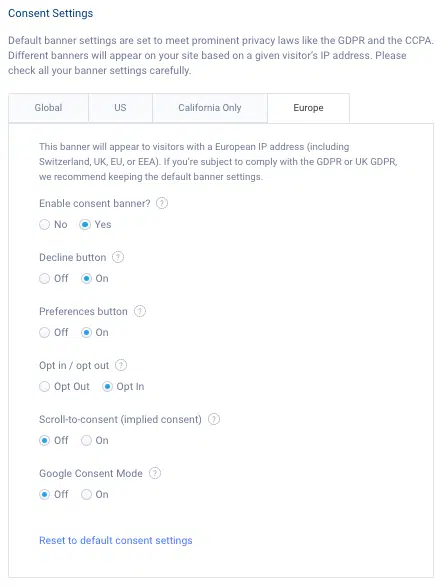
We also offer a Consent Management Platform equipped with regional support settings so you can configure a GDPR-compliant consent banner that appears for all of your EU/EEA users and adequately obtains and tracks their consent choices following the regulation.
In the screenshot below, you can see an example of the settings for our consent banner.
We’re your all-in-one compliance solution, and our tools help small to medium-sized businesses around the globe remain up-to-date with laws like the GDPR and more.
Summary
The GDPR changed the scope of data privacy forever and has affected businesses worldwide.
But with this guide and Termly in your toolbox, you’re ready to set your website up for full compliance without any hassles, confusion, and expensive legal fees.
Remember, to comply with this regulation, you’ll need a compliant privacy and cookie policy, a properly configured consent banner, and a DSAR form on your website.
For more in-depth help with the GDPR, check out these valuable resources:
- What Is the GDPR? — Our more comprehensive guide to everything you need to know about the GDPR.
- EU GDPR Homepage — The official GDPR website features helpful information if you want to dig deeper into the legal stuff.
- The ICO’s GDPR Guide — This UK authority’s guide is helpful for all businesses.
Reviewed by Masha Komnenic CIPP/E, CIPM, CIPT, FIP Director of Global Privacy