Businesses under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are responsible for receiving and responding to requests from individuals to follow through on their privacy rights, also called a data subject access request (DSAR).
Your business should establish a formal internal procedure for how your team will navigate DSARs from GDPR data subjects in a timely and legally compliant manner.
In this guide, I provide you with the GDPR requirements for DSARs and walk you through steps your business can take to simplify and streamline your response process.
GDPR’s Definition of Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs)
Under Article 15 of the GDPR, a DSAR refers to when a protected individual (aka, the data subject) submits a request to access the personal data a company collected about them.
You might also see these referred to as subject access requests or SARs.
The ‘A’ in ‘DSAR’ stands for ‘Access.’
However, individuals can submit DSARs to follow through on any of the privacy rights given to them by the GDPR.
They can submit requests in any way, including email, telephone, or social media.
But if the data subject makes the request by electronic means, unless otherwise requested by the data subject, the information shall be provided in a commonly used electronic form.
It helps to provide a properly titled DSAR form on your website, which will filter most of your users’ requests into a single channel and make the process more efficient.
However, you still need to check for DSARs in other communication avenues just in case a consumer sends their request elsewhere.
What Rights Does the GDPR Give Data Subjects?
The GDPR outlines the rights of the data subject in Chapter 3, Articles 12 – 23, which include the following:
- Access personal data (Article 15);
- Rectify personal data (Article 16);
- Erasure/the right to be forgotten (Article 17);
- Restrict the processing of data (Article 18);
- Data portability (Article 20);
- Object to data processing (Article 21);
- Object to individual decision-making and profiling (Article 22).
You must be prepared to respond to DSARs for any of these rights in a timely manner, following all rules and principles outlined by the Regulation.
How To Navigate the GDPR and DSARs: Step-by-Step
To simplify navigating a DSAR from a GDPR data subject, I recommend your business follows these five easy steps.
Step 1: Verification Requirements
After receiving a DSAR from a GDPR data subject, the first step is to acknowledge and confirm the receipt of the request to the individual that had submitted it and ensure you can adequately verify their identity.
Verification of identity is required because, legally, you cannot release information about another person to an unauthorized individual.
According to Recital 64 of the GDPR, you get to decide how to verify a user identity but must use all “reasonable measures” in the context of the online services and online identifiers.
But you cannot retain personal data for the sole purpose of verifying consumer requests for DSAR purposes, and you should not ask for additional information.
You must find ways to verify their identity using the data you’ve already collected from them and not ask for more details, especially sensitive personal data.
For example, if you had only collected the name and e-mail address of a data subject, do not ask them for a copy of their ID or password just to legitimize them.
Common ways businesses verify the identity of GDPR subjects who submit DSARs include:
- Asking questions based on the data you already have about them;
- Using a previously confirmed method of validation, like an email address;
- Determining the last ways the user interacted with your site, product, or service.
Once you know the data subject is who they claim to be, you can move on to the next step.
Step 2: Information to Include in a Response
Next, your business should establish a process for safely locating and gathering consumer data when responding to a DSAR.
Ensure you address all aspects of their request; for example, they may want to access their data and correct a misspelling of their last name.
To help simplify this step, consider performing a data audit to locate all personal data your company collects and stores.
Consider these guidelines for legal reasons and to prevent potential data breaches:
- Limit who responds to DSARs and who has access to personal data;
- Know where all personal data is stored, both digitally and physically;
- Make sure you locate and include all data the user requested;
- Don’t store personal data for longer than necessary;
- But do keep a log of your DSAR responses in case of a future audit
In some scenarios, you may also need to censor parts of the information you’re about to disclose when responding to a request.
For example, you might do so to protect the data of another person who’s not the requester. You can only disclose personal data pertaining to another person if you have their consent.
Step 3: Timeline for Responding
Under the GDPR, you have one month to respond to a DSAR, which can be extended by an additional two further months if:
- The request is complex and you need time to investigate;
- You receive multiple requests and your resources are limited;
- The request is unclear and you need more information.
The GDPR outlines this specific timeline for responding to DSARs in Article 12, Section 3.
Make sure the people on your team responsible for responding to DSARs are aware of these time constraints.
Equally important, you should not wait until the last day to provide the reply. You should reply as soon as possible within the one-month deadline.
As mentioned above, it is of paramount importance to send a response acknowledging that you’ve received the data subject’s request and are working on your response; this helps you meet the requirements outlined by the GDPR and reassures the consumer.
Step 4: Refusing to Respond
The GDPR allows you to refuse to respond to a DSAR in a few circumstances and should establish a process for determining when a request falls within these boundaries.
For example, if the request is unreasonable, excessive, manifestly unfounded, or breaches another person’s privacy rights, you can deny it.
You must inform the requester promptly of your choice, and you are responsible for proving the request was unfounded should a supervisory authority question you or the data subject initiates a claim before a national court against you.
Data subjects may then submit an appeal to your decision based on their DSAR, so ensure you have a similar process set up that’s just as easy for consumers.
Step 5: Keep a Log of Your Responses
Finally, make sure you’re keeping a log of all your DSAR responses just in case a supervisory authority audits you or as already mentioned, the case is brought by the data subject before a court.
Nonetheless, you should not keep this log for an indefinite period of time. A period of 12-24 months can be considered as reasonable.
Make sure you store this information in a secure environment so it’s safe from data breaches and unauthorized access.
Using Termly for the GDPR’s DSAR Requirements
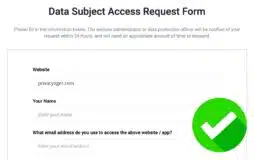
If your business needs to comply with the GDPR, Termly’s Consent Management Platform provides you with a free embeddable DSAR form you can add directly to your website.
The DSAR form allows your users to input essential details to help streamline your response process, including:
- Which privacy law they are protected by;
- Which right(s) they want to follow through on;
- Which email address they use to commonly contact your website.
The form encourages users to provide you with enough information so you can verify their identity following the GDPR and respond within the one month timeframe.
Summary
Responding to DSARs is part of the course for businesses under the GDPR, but navigating the requirements is much easier if your business implements a formal internal DSAR process.
Ensure your team knows how to verify the identities of data subjects who submit DSARs without breaching the rules and principles of the Regulation, and respond to DSARs within the month-long time limit.
Make it extra easy for your business and consumers by providing them with an accessible DSAR form on your website.